Orf
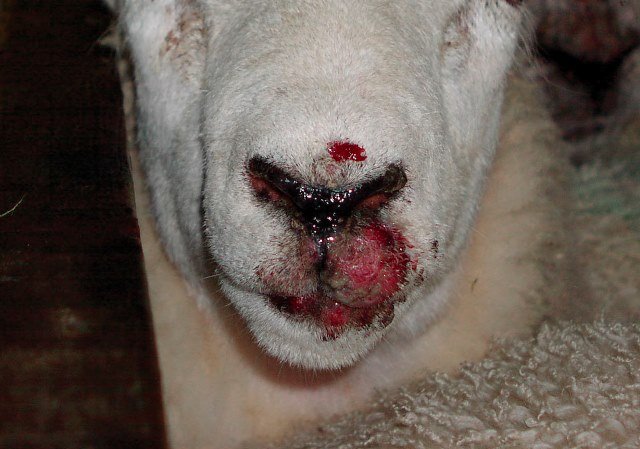
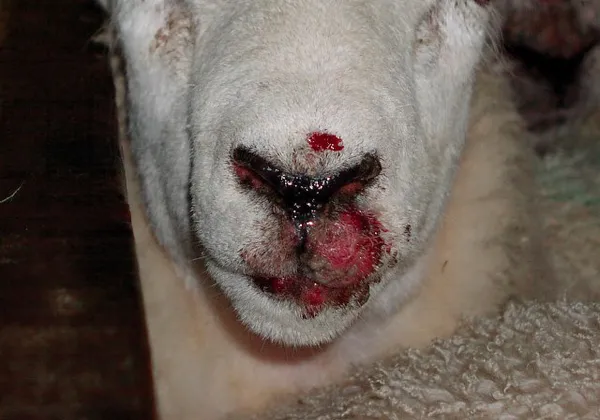
Orf, also known as Contagious Pustular Dermatitis, is a highly contagious viral skin disease that primarily affects sheep and goats. It is caused by a parapoxvirus and is prevalent in many parts of the world. The disease is particularly common in young lambs but can also affect adult sheep, especially around the mouth, udder, and lower legs.
Symptoms and diagnosis of Orf in sheep🩺
Common symptoms of Orf in sheep
- Scabby lesions around the mouth and nostrils of lambs.
- Lesions can also appear on the gums, around the eyes, and ears.
- Infected teats in ewes, leading to mastitis.
- Lesions on the lower legs of lambs.
The lesions start as blisters and progress to bleeding, scabbed-over areas of damaged skin. Secondary bacterial infections are common and can increase the recovery time from the Orf virus.
How to diagnose Orf in sheep
Diagnosis is typically based on the presence of characteristic lesions. In some cases, laboratory confirmation may be required. This can be done through electron microscopy of fresh lesions or PCR tests to detect the viral DNA.
How to treat Orf in sheep💊
Unfortunately, there is no practical method to kill the virus once it has infected the animal. Treatment focuses on minimizing secondary bacterial infections and ensuring the animal can feed properly. Here are some steps you can take:
- Use topical antibiotic sprays and injections in severe cases to minimize the risk of secondary bacterial infections.
- Provide pain relief to severely affected lambs.
- Ensure good nutrition to prevent weight loss in lambs having difficulty sucking.
How to prevent Orf 🛡️
Orf Vaccination for sheep
There is an effective vaccine available that consists of a live virus. This vaccine should only be used in flocks that have had Orf diagnosed, as the formed scabs can contaminate the environment. The vaccine should be applied to ewes eight weeks before lambing, and the ewes should be kept away from the lambing area until the scabs are shed. Lambs should be vaccinated shortly after birth, usually as they are turned out.
Hygiene and Management
- Thoroughly clean and disinfect buildings, especially wooden structures, as the virus can persist in buildings for many years.
- Ensure good hygiene practices, such as wearing gloves when handling affected sheep, as Orf is zoonotic and can infect humans.
Environmental Control
Infection will only establish where the skin or gums have already been damaged. Thus, rough food or pasture full of thistles may make sheep more prone to infection. Attention to feeding and avoiding rough pastures can help in preventing the disease.